Welcome








at RWTH Aachen University!
The Virtual Reality and Immersive Visualization Group started in 1998 as a service team in the RWTH IT Center. Since 2015, we are a research group (Lehr- und Forschungsgebiet) at i12 within the Computer Science Department. Moreover, the Group is a member of the Visual Computing Institute and continues to be an integral part of the RWTH IT Center.
In a unique combination of research, teaching, services, and infrastructure, we provide Virtual Reality technologies and the underlying methodology as a powerful tool for scientific-technological applications.
In terms of basic research, we develop advanced methods and algorithms for multimodal 3D user interfaces and explorative analyses in virtual environments. Furthermore, we focus on application-driven, interdisciplinary research in collaboration with RWTH Aachen institutes, Forschungszentrum Jülich, research institutions worldwide, and partners from business and industry, covering fields like simulation science, production technology, neuroscience, and medicine.
To this end, we are members of / associated with the following institutes and facilities:
 | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
 | |
Our offices are located in the RWTH IT Center, where we operate one of the largest Virtual Reality labs worldwide. The aixCAVE, a 30 sqm visualization chamber, makes it possible to interactively explore virtual worlds, is open to use by any RWTH Aachen research group.
News
| • |
Sevinc Eroglu receives doctoral degree from RWTH Aachen University Today, our former colleague Sevinc Eroglu successfully passed her Ph.D. defense and received a doctoral degree from RWTH Aachen University for her thesis on "Building Immersive Worlds: Authoring Content and Interactivity in VR". Congratulations! |
Jan. 9, 2026 |
| • |
Jonathan Ehret receives doctoral degree from RWTH Aachen University Today, our former colleague Jonathan Ehret successfully passed his Ph.D. defense and received a doctoral degree from RWTH Aachen University for his thesis on "Enhancing Social Presence in Embodied Conversational Agents: A Multimodal Approach to Natural Communication". Congratulations! |
Dec. 8, 2025 |
| • |
Martin Bellgardt receives doctoral degree from RWTH Aachen University Today, our former colleague Martin Bellgardt successfully passed his Ph.D. defense and received a doctoral degree from RWTH Aachen University for his thesis on "Increasing Immersion in Machine Learning Pipelines for Mechanical Engineering". Congratulations! |
April 30, 2025 |
| • |
Active Participation at 2024 IEEE VIS Conference (VIS 2024) At this year's IEEE VIS Conference, several contributions of our visualization group were presented. Dr. Tim Gerrits chaired the 2024 SciVis Contest and presented two accepted papers: The short paper "DaVE - A Curated Database of Visualization Examples" by Jens Koenen, Marvin Petersen, Christoph Garth and Dr. Tim Gerrits as well as the contribution to the Workshop on Uncertainty Exploring Uncertainty Visualization for Degenerate Tensors in 3D Symmetric Second-Order Tensor Field Ensembles by Tadea Schmitz and Dr. Tim Gerrits, which was awarded the best paper award. Congratulations! |
Oct. 22, 2024 |
| • |
Honorable Mention One Best Paper Honorable Mention Award of the VRST 2024 was given to Sevinc Eroglu for her paper entitled “Choose Your Reference Frame Right: An Immersive Authoring Technique for Creating Reactive Behavior”. |
Oct. 11, 2024 |
| • |
Tim Gerrits as invited Keynote Speaker at the ParaView User Days in Lyon ParaView, developed by Kitware is one of the most-used open-source visualization and analysis tools, widely used in research and industry. For the second edition of the ParaView user days, Dr. Tim Gerrits was invited to share his insights of developing and providing visualization within the academic communities. |
Sept. 26, 2024 |
Recent Publications
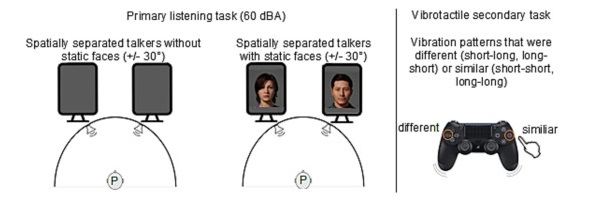 Beyond Words: The Impact of Static and Animated Faces as Visual Cues on Memory Performance and Listening Effort during Two-Talker Conversations Acta Psychologica Listening to a conversation between two talkers and recalling the information is a common goal in verbal communication. However, cognitive-psychological experiments on short-term memory performance often rely on rather simple stimulus material, such as unrelated word lists or isolated sentences. The present study uniquely incorporated running speech, such as listening to a two-talker conversation, to investigate whether talker-related visual cues enhance short-term memory performance and reduce listening effort in non-noisy listening settings. In two equivalent dual-task experiments, participants listened to interrelated sentences spoken by two alternating talkers from two spatial positions, with talker-related visual cues presented as either static faces (Experiment 1, n = 30) or animated faces with lip sync (Experiment 2, n = 28). After each conversation, participants answered content-related questions as a measure of short-term memory (via the Heard Text Recall task). In parallel to listening, they performed a vibrotactile pattern recognition task to assess listening effort. Visual cue conditions (static or animated faces) were compared within-subject to a baseline condition without faces. To account for inter-individual variability, we measured and included individual working memory capacity, processing speed, and attentional functions as cognitive covariates. After controlling for these covariates, results indicated that neither static nor animated faces improved short-term memory performance for conversational content. However, static faces reduced listening effort, whereas animated faces increased it, as indicated by secondary task RTs. Participants' subjective ratings mirrored these behavioral results. Furthermore, working memory capacity was associated with short-term memory performance, and processing speed was associated with listening effort, the latter reflected in performance on the vibrotactile secondary task. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that visual cues influence listening effort and that individual differences in working memory and processing speed help explain variability in task performance, even in optimal listening conditions. 
|
 Objectifying Social Presence: Evaluating Multimodal Degraders in ECAs Using the Heard Text Recall Paradigm IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics
Embodied conversational agents (ECAs) are key social interaction partners in various virtual reality (VR) applications, with their perceived social presence significantly influencing the quality and effectiveness of user-ECA interactions. This paper investigates the potential of the Heard Text Recall (HTR) paradigm as an indirect objective proxy for evaluating social presence, which is traditionally assessed through subjective questionnaires. To this end, we use the HTR task, which was primarily designed to assess memory performance in listening tasks, in a dual-task paradigm to assess cognitive spare capacity and correlate the latter with subjectively-rated social presence. As a prerequisite for this investigation, we introduce various co-verbal gesture modification techniques and assess their impact on the perceived naturalness of the presenting ECA, a crucial aspect fostering social presence. The main study then explores the applicability of HTR as a proxy for social presence by examining its effectiveness under different multimodal degraders of ECA behavior, including degraded co-verbal gestures, omitted lip synchronization, and the use of synthetic voices. The findings suggest that while HTR shows potential as an objective measure of social presence, its effectiveness is primarily evident in response to substantial changes in ECA behavior. Additionally, the study also highlights the negative effects of synthetic voices and inadequate lip synchronization on perceived social presence, emphasizing the need for careful consideration of these elements in ECA design. 
|
 Heard-Text Recall and Listening Effort under Irrelevant Speech and Pseudo-Speech in Virtual Reality Acta Acustica
**Introduction**: Verbal communication depends on a listener’s ability to accurately comprehend and recall information conveyed in a conversation. The heard-text recall (HTR) paradigm can be used in a dual-task design to assess both memory performance and listening effort. In contrast to traditional tasks such as serial recall, this paradigm uses running speech to simulate a conversation between two talkers. Thereby, it allows for talker visualization in virtual reality (VR), providing co-verbal visual cues like lip-movements, turn-taking cues, and gaze behavior. While this paradigm has been investigated under pink noise, the impact of more realistic irrelevant stimuli, such as speech, that provide temporal fluctuations and meaning compared to noise, remains unexplored. 
|

