Publications
DaVE - A Curated Database of Visualization Examples

While mobile devices have developed into hardware with advanced capabilities for rendering 3D gra-phics, they commonly lack the computational power to render large 3D scenes with complex lighting interactively. A prominent approach to tackle this is rendering required views on a remote server and streaming them to the mobile client. However, the rate at which servers can supply data is limited, e.g., by the available network speed, requiring image-based rendering techniques like image warping to compensate for the latency and allow a smooth user experience, especially in scenes where rapid user movement is essential. In this paper, we present a novel streaming approach designed to minimize arti-facts during the warping process by including an additional visibility layer that keeps track of occluded surfaces while allowing access to 360° views. In addition, we propose a novel mesh generation techni-que based on the detection of loops to reliably create a mesh that encodes the depth information requi-red for the image warping process. We demonstrate our approach in a number of complex scenes and compare it against existing works using two layers and one layer alone. The results indicate a significant reduction in computation time while achieving comparable or even better visual results when using our dual-layer approach.
Towards Comprehensible and Expressive Teleportation Techniques in Immersive Virtual Environments

Teleportation, a popular navigation technique in virtual environments, is favored for its efficiency and reduction of cybersickness but presents challenges such as reduced spatial awareness and limited navigational freedom compared to continuous techniques. I would like to focus on three aspects that advance our understanding of teleportation in both the spatial and the temporal domain. 1) An assessment of different parametrizations of common mathematical models used to specify the target location of the teleportation and the influence on teleportation distance and accuracy. 2) Extending teleportation capabilities to improve navigational freedom, comprehensibility, and accuracy. 3) Adapt teleportation to the time domain, mediating temporal disorientation. The results will enhance the expressivity of existing teleportation interfaces and provide validated alternatives to their steering-based counterparts.
Exploring Gaze Dynamics: Initial Findings on the Role of Listening Bystanders in Conversational Interactions
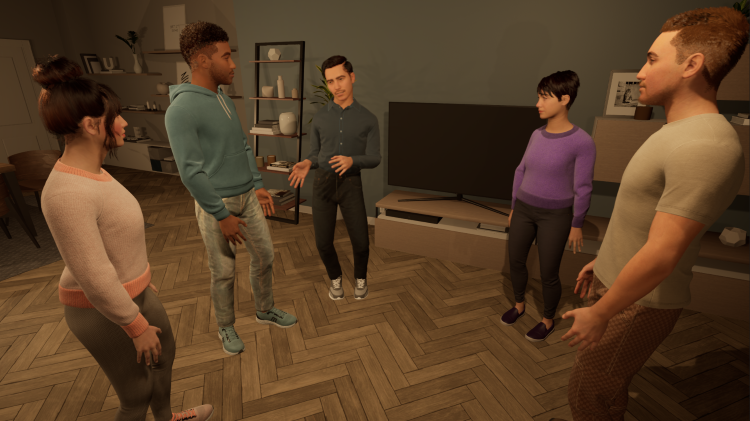

This work-in-progress paper investigates how virtual listening bystanders influence participants’ gaze behavior and their perception of turn-taking during scripted conversations with embodied conversational agents (ECAs). 25 participants interacted with five ECAs – two speakers and three bystanders – across three conditions: no bystanders, bystanders exhibiting random gazing behavior, and social bystanders engaging in mutual gaze and backchanneling. Participants either observed the conversation or actively participated as speakers by reciting prompted sentences. The results indicated that bystanders reduced the participants’ attention to speakers, hindering their ability to anticipate turn changes and resulting in longer delays in shifting their gaze to the new speaker after an ECA yielded the turn. Random gazing bystanders were particularly noted for obscuring conversational flow. These findings underscore the challenges of designing effective and natural conversational environments, highlighting the need for careful consideration of ECA behaviors to enhance user engagement.
@INPROCEEDINGS{Ehret2025,
author={Ehret, Jonathan and Dasbach, Valentin and Hartmann, Jan-Nikjas and
Fels, Janina and Kuhlen, Torsten W. and Bönsch, Andrea},
booktitle={2025 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces
Abstracts and Workshops (VRW)},
title={Exploring Gaze Dynamics: Initial Findings on the Role of Listening
Bystanders in Conversational Interactions},
year={2025},
volume={},
number={},
pages={748-752},
doi={10.1109/VRW66409.2025.00151}}
Front Matter: 9th Edition of IEEE VR Workshop: Virtual Humans and Crowds in Immersive Environments (VHCIE)

The VHCIE workshop aims to explore and advance the creation of believable virtual humans and crowds within immersive virtual environments (IVEs). With the emergence of various tools, algorithms, and systems, it is now possible to design realistic virtual characters - known as virtual agents (VAs) - that can populate expansive environments with thousands of individuals. These sophisticated crowd simulations facilitate dynamic interactions among the VAs themselves and between VAs and virtual reality (VR) users. The VHCIE workshop seeks to highlight the diverse range of VR applications for these advancements, including virtual tour guides, platforms for professional training, studies on human behavior, and even recreations of live events like concerts. By fostering discussions around these themes, VHCIE aims to inspire innovative approaches and collaborative efforts that push the boundaries of what is possible in social IVEs while also providing an open place for networking and exchanging ideas among participants. Bild: Bitte das VHCIE Logo im Anhang nutzen und klein rechts in die Ecke packen
@INPROCEEDINGS{Boensch2025,
author={Bönsch, Andrea and Chollet, Mathieu and Martin, Jordan and
Olivier, Anne-Hélène and Pettré, Julien},
booktitle={2025 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces
Abstracts and Workshops (VRW)},
title={9th Edition of IEEE VR Workshop: Virtual Humans and Crowds in
Immersive Environments (VHCIE)},
year={2025},
volume={},
number={},
pages={703-704},
doi={10.1109/VRW66409.2025.00142}
}
Geschichte(n) in Virtual Reality - Perspektiven der Informatik

Den Bau der Pyramiden von Gizeh beobachten – und dann gleich weiter ins antike Rom? Das und mehr soll mit Virtual Reality möglich werden. Doch was macht das mit unserem Verständnis von Geschichte?
Virtual-Reality-Anwendungen mit historischem Inhalt haben Konjunktur. Sie versprechen virtuelle Zeitreisen und die Möglichkeit, endlich zeigen zu können, wie die Vergangenheit wirklich war. Daraus resultieren Formen des Umgangs mit Geschichte, die nicht nur die außerschulische Geschichtskultur und -vermittlung prägen, sondern auch zunehmend in den Geschichtsunterricht hineinwirken. Im Zentrum dieses Bandes steht daher die Frage: Was macht Virtual Reality mit Geschichte? Während aus Sicht der Informatik historische Inhalte »nur« besondere Gestaltungskriterien mit sich bringen, sieht sich die Geschichtswissenschaft mit einer Konkurrenz im Bereich der Geschichtsdarstellung konfrontiert, die womöglich sogar droht, diese obsolet zu machen. Museen und Gedenkstätten sehen sich mit der Aufgabe konfrontiert, VR-Anwendungen in ihr Angebot einzubinden und trotzdem – oder gerade damit – Besuchende für ihre Institutionen zu gewinnen. Die Geschichtsdidaktik diskutiert vor diesem Hintergrund die Folgen virtueller Darstellungen innerhalb und außerhalb des Unterrichts auf historische Lernprozesse. Zu Wort kommen Expert:innen aus den genannten Fachbereichen, um ihre Perspektive auf die Frage darzulegen: Ist Virtual Reality die Zukunft der historischen Bildung?
Front Matter: The Third Workshop on Locomotion and Wayfinding in XR (LocXR)
The Third Workshop on Locomotion and Wayfinding in XR, held in conjunction with IEEE VR 2025 in Saint-Malo, France, is dedicated to advancing research and fostering discussions around the critical topics of navigation in extended reality (XR). Navigation is a fundamental form of user interaction in XR, yet it poses numerous challenges in conceptual design, technical implementation, and systematic evaluation. By bringing together researchers and practitioners, this workshop aims to address these challenges and push the boundaries of what is achievable in XR navigation.
@inproceedings{Weissker2025,
author={T. {Weissker} and D. {Zielasko}},
booktitle={2025 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (VRW)},
title={The Third Workshop on Locomotion and Wayfinding in XR (LocXR)},
year={2025},
volume={},
number={},
pages={239-240},
doi={10.1109/VRW66409.2025.00058}
}
PASCAL - A Collaboration Technique Between Non-Collocated Avatars in Large Collaborative Virtual Environments
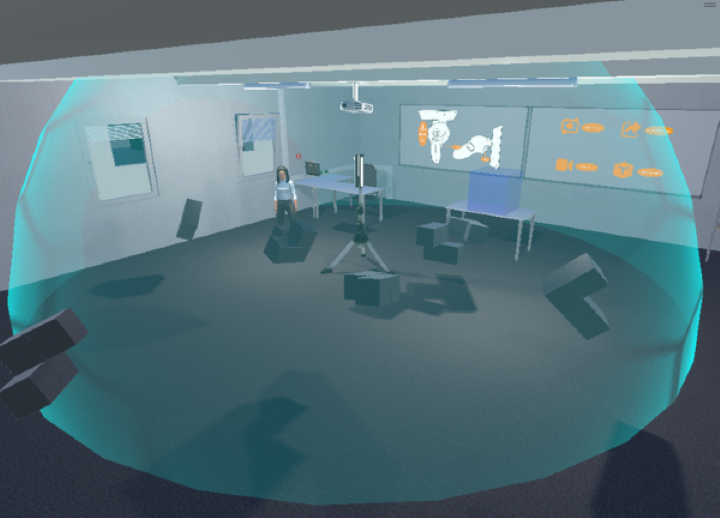
Collaborative work in large virtual environments often requires transitions from loosely-coupled collaboration at different locations to tightly-coupled collaboration at a common meeting point. Inspired by prior work on the continuum between these extremes, we present two novel interaction techniques designed to share spatial context while collaborating over large virtual distances. The first method replicates the familiar setup of a video conference by providing users with a virtual tablet to share video feeds with their peers. The second method called PASCAL (Parallel Avatars in a Shared Collaborative Aura Link) enables users to share their immediate spatial surroundings with others by creating synchronized copies of it at the remote locations of their collaborators. We evaluated both techniques in a within-subject user study, in which 24 participants were tasked with solving a puzzle in groups of two. Our results indicate that the additional contextual information provided by PASCAL had significantly positive effects on task completion time, ease of communication, mutual understanding, and co-presence. As a result, our insights contribute to the repertoire of successful interaction techniques to mediate between loosely- and tightly-coupled work in collaborative virtual environments.
@article{Gilbert2025,
author={D. {Gilbert} and A. {Bose} and T. {Kuhlen} and T. {Weissker}},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics},
title={PASCAL - A Collaboration Technique Between Non-Collocated Avatars in Large Collaborative Virtual Environments},
year={2025},
volume={31},
number={5},
pages={1268-1278},
doi={10.1109/TVCG.2025.3549175}
}
Minimalism or Creative Chaos? On the Arrangement and Analysis of Numerous Scatterplots in Immersi-ve 3D Knowledge Spaces
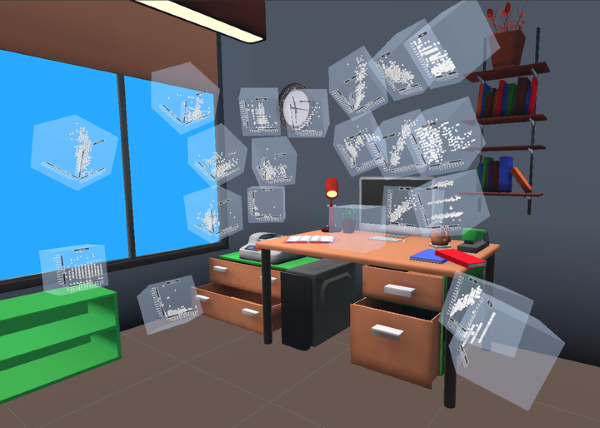

Working with scatterplots is a classic everyday task for data analysts, which gets increasingly complex the more plots are required to form an understanding of the underlying data. To help analysts retrieve relevant plots more quickly when they are needed, immersive virtual environments (iVEs) provide them with the option to freely arrange scatterplots in the 3D space around them. In this paper, we investigate the impact of different virtual environments on the users' ability to quickly find and retrieve individual scatterplots from a larger collection. We tested three different scenarios, all having in common that users were able to position the plots freely in space according to their own needs, but each providing them with varying numbers of landmarks serving as visual cues - an Emptycene as a baseline condition, a single landmark condition with one prominent visual cue being a Desk, and a multiple landmarks condition being a virtual Office. Results from a between-subject investigation with 45 participants indicate that the time and effort users invest in arranging their plots within an iVE had a greater impact on memory performance than the design of the iVE itself. We report on the individual arrangement strategies that participants used to solve the task effectively and underline the importance of an active arrangement phase for supporting the spatial memorization of scatterplots in iVEs.
@article{Derksen2025,
author={M. {Derksen} and T. {Kuhlen} and M. {Botsch} and T. {Weissker}},
journal={IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics},
title={Minimalism or Creative Chaos? On the Arrangement and Analysis of Numerous Scatterplots in Immersive 3D Knowledge Spaces},
year={2025},
volume={31},
number={5},
pages={746-756},
doi={10.1109/TVCG.2025.3549546}
}
Previous Year (2024)

