Advantages of a Training Course for Surgical Planning in Virtual Reality in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
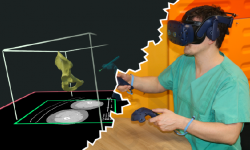
Background: As an integral part of computer-assisted surgery, virtual surgical planning(VSP) leads to significantly better surgery results, such as for oral and maxillofacial reconstruction with microvascular grafts of the fibula or iliac crest. It is performed on a 2D computer desktop (DS) based on preoperative medical imaging. However, in this environment, VSP is associated with shortcomings, such as a time-consuming planning process and the requirement of a learning process. Therefore, a virtual reality VR)-based VSP application has great potential to reduce or even overcome these shortcomings due to the benefits of visuospatial vision, bimanual interaction, and full immersion. However, the efficacy of such a VR environment has not yet been investigated.
Objective: Does VR offer advantages in learning process and working speed while providing similar good results compared to a traditional DS working environment?
Methods: During a training course, novices were taught how to use a software application in a DS environment (3D Slicer) and in a VR environment (Elucis) for the segmentation of fibulae and os coxae (n = 156), and they were askedto carry out the maneuvers as accurately and quickly as possible. The individual learning processes in both environments were compared usingobjective criteria (time and segmentation performance) and self-reported questionnaires. The models resulting from the segmentation were compared mathematically (Hausdorff distance and Dice coefficient) and evaluated by two experienced radiologists in a blinded manner (score).
Results: During a training course, novices were taught how to use a software application in a DS environment (3D Slicer) and in a VR environment (Elucis)for the segmentation of fibulae and os coxae (n = 156), and they were asked to carry out the maneuvers as accurately and quickly as possible. The individual learning processes in both environments were compared using objective criteria (time and segmentation performance) and self-reported questionnaires. The models resulting from the segmentation were compared mathematically (Hausdorff distance and Dice coefficient) and evaluated by two experienced radiologists in a blinded manner (score).
Conclusions: The more rapid learning process and the ability to work faster in the VR environment could save time and reduce the VSP workload, providing certain advantages over the DS environment.
@article{Ulbrich2022,
title={Advantages of a Training Course for Surgical Planning in Virtual
Reality in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery },
author={ Ulbrich, M., Van den Bosch, V., Bönsch, A., Gruber, L.J., Ooms,
M., Melchior, C., Motmaen, I., Wilpert, C., Rashad, A., Kuhlen, T.W.,
Hölzle, F., Puladi, B.},
journal={JMIR Serious Games},
volume={ 28/11/2022:40541 (forthcoming/in press) },
year={2022},
publisher={JMIR Publications Inc., Toronto, Canada}
}

