Profile

|
Ali Can Demiralp, M. Sc. |
Publications
Insite: A Pipeline Enabling In-Transit Visualization and Analysis for Neuronal Network Simulations
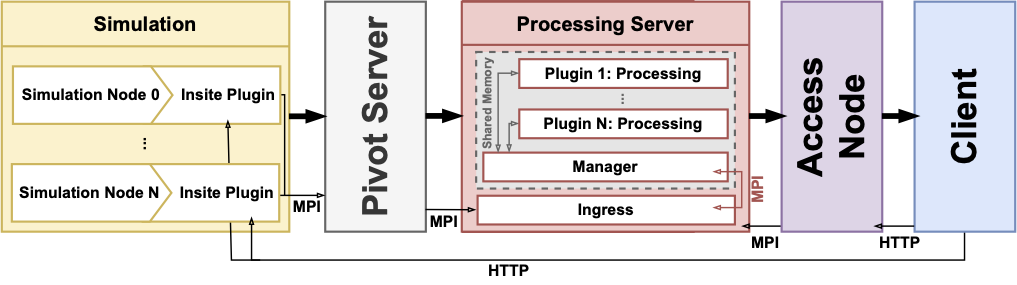
Neuronal network simulators are central to computational neuroscience, enabling the study of the nervous system through in-silico experiments. Through the utilization of high-performance computing resources, these simulators are capable of simulating increasingly complex and large networks of neurons today. Yet, the increased capabilities introduce a challenge to the analysis and visualization of the simulation results. In this work, we propose a pipeline for in-transit analysis and visualization of data produced by neuronal network simulators. The pipeline is able to couple with simulators, enabling querying, filtering, and merging data from multiple simulation instances. Additionally, the architecture allows user-defined plugins that perform analysis tasks in the pipeline. The pipeline applies traditional REST API paradigms and utilizes data formats such as JSON to provide easy access to the generated data for visualization and further processing. We present and assess the proposed architecture in the context of neuronal network simulations generated by the NEST simulator.
@InProceedings{10.1007/978-3-031-23220-6_20,
author="Kr{\"u}ger, Marcel and Oehrl, Simon and Demiralp, Ali C. and Spreizer, Sebastian and Bruchertseifer, Jens and Kuhlen, Torsten W. and Gerrits, Tim and Weyers, Benjamin",
editor="Anzt, Hartwig and Bienz, Amanda and Luszczek, Piotr and Baboulin, Marc",
title="Insite: A Pipeline Enabling In-Transit Visualization and Analysis for Neuronal Network Simulations",
booktitle="High Performance Computing. ISC High Performance 2022 International Workshops",
year="2022",
publisher="Springer International Publishing",
address="Cham",
pages="295--305",
isbn="978-3-031-23220-6"
}
Performance Assessment of Diffusive Load Balancing for Distributed Particle Advection
Particle advection is the approach for the extraction of integral curves from vector fields. Efficient parallelization of particle advection is a challenging task due to the problem of load imbalance, in which processes are assigned unequal workloads, causing some of them to idle as the others are performing computing. Various approaches to load balancing exist, yet they all involve trade-offs such as increased inter-process communication, or the need for central control structures. In this work, we present two local load balancing methods for particle advection based on the family of diffusive load balancing. Each process has access to the blocks of its neighboring processes, which enables dynamic sharing of the particles based on a metric defined by the workload of the neighborhood. The approaches are assessed in terms of strong and weak scaling as well as load imbalance. We show that the methods reduce the total run-time of advection and are promising with regard to scaling as they operate locally on isolated process neighborhoods.
Astray: A Performance-Portable Geodesic Ray Tracer
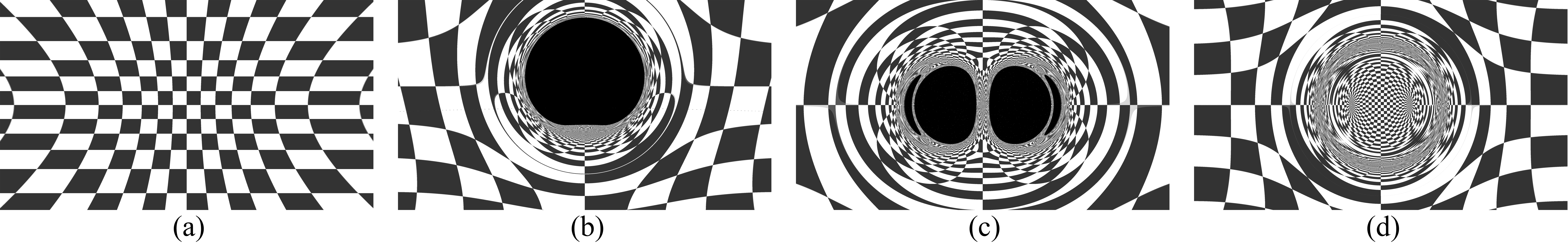
Geodesic ray tracing is the numerical method to compute the motion of matter and radiation in spacetime. It enables visualization of the geometry of spacetime and is an important tool to study the gravitational fields in the presence of astrophysical phenomena such as black holes. Although the method is largely established, solving the geodesic equation remains a computationally demanding task. In this work, we present Astray; a high-performance geodesic ray tracing library capable of running on a single or a cluster of computers equipped with compute or graphics processing units. The library is able to visualize any spacetime given its metric tensor and contains optimized implementations of a wide range of spacetimes, including commonly studied ones such as Schwarzschild and Kerr. The performance of the library is evaluated on standard consumer hardware as well as a compute cluster through strong and weak scaling benchmarks. The results indicate that the system is capable of reaching interactive frame rates with increasing use of high-performance computing resources. We further introduce a user interface capable of remote rendering on a cluster for interactive visualization of spacetimes.
@inproceedings {10.2312:vmv.20221208,
booktitle = {Vision, Modeling, and Visualization},
editor = {Bender, Jan and Botsch, Mario and Keim, Daniel A.},
title = {{Astray: A Performance-Portable Geodesic Ray Tracer}},
author = {Demiralp, Ali Can and Krüger, Marcel and Chao, Chu and Kuhlen, Torsten W. and Gerrits, Tim},
year = {2022},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
ISBN = {978-3-03868-189-2},
DOI = {10.2312/vmv.20221208}
}
MODE: A modern ordinary differential equation solver for C++ and CUDA
Ordinary differential equations (ODE) are used to describe the evolution of one or more dependent variables using their derivatives with respect to an independent variable. They arise in various branches of natural sciences and engineering. We present a modern, efficient, performance-oriented ODE solving library built in C++20. The library implements a broad range of multi-stage and multi-step methods, which are generated at compile-time from their tableau representations, avoiding runtime overhead. The solvers can be instantiated and iterated on the CPU and the GPU using identical code. This work introduces the prominent features of the library with examples
Poster: A C++20 Interface for MPI 4.0
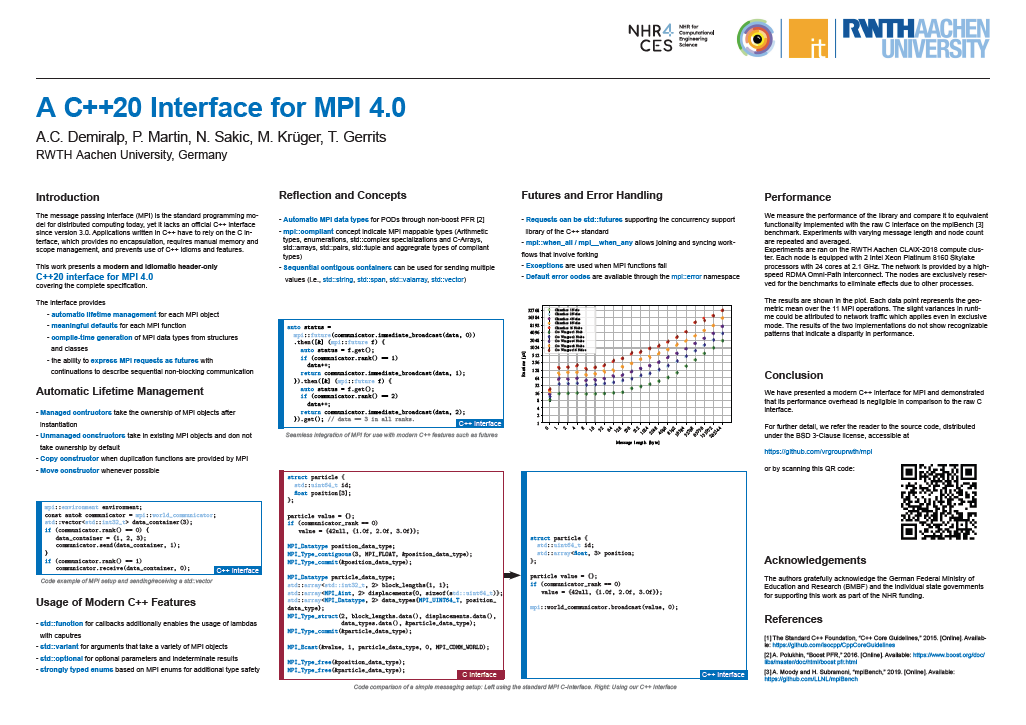
We present a modern C++20 interface for MPI 4.0. The interface utilizes recent language features to ease development of MPI applications. An aggregate reflection system enables generation of MPI data types from user-defined classes automatically. Immediate and persistent operations are mapped to futures, which can be chained to describe sequential asynchronous operations and task graphs in a concise way. This work introduces the prominent features of the interface with examples. We further measure its performance overhead with respect to the raw C interface.
@misc{demiralp2023c20,
title={A C++20 Interface for MPI 4.0},
author={Ali Can Demiralp and Philipp Martin and Niko Sakic and Marcel Krüger and Tim Gerrits},
year={2023},
eprint={2306.11840},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.DC}
}
Talk: Insite: A Generalized Pipeline for In-transit Visualization and Analysis
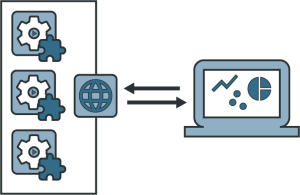
Neuronal network simulators are essential to computational neuroscience, enabling the study of the nervous system through in-silico experiments. Through utilization of high-performance computing resources, these simulators are able to simulate increasingly complex and large networks of neurons today. It also creates new challenges for the analysis and visualization of such simulations. In-situ and in-transport strategies are popular approaches in these scenarios. They enable live monitoring of running simulations and parameter adjustment in the case of erroneous configurations which can save valuable compute resources.
This talk will present the current status of our pipeline for in-transport analysis and visualization of neuronal network simulator data. The pipeline is able to couple with NEST along other simulators with data management (querying, filtering and merging) from multiple simulator instances. Finally, the data is passed to end-user applications for visualization and analysis. The goal is to be integrated into third party tools such as the multi-view visual analysis toolkit ViSimpl.
Voxel-Based Edge Bundling Trough Direction-Aware Kernel Smoothing
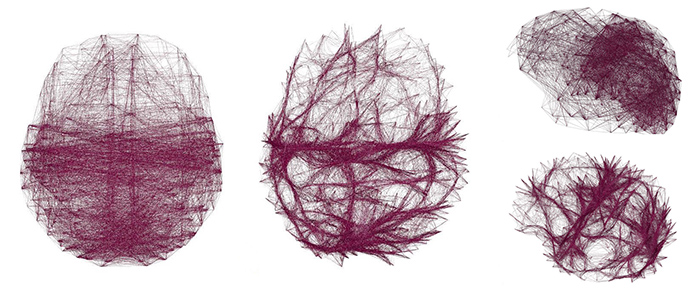
Relational data with a spatial embedding and depicted as node-link diagram is very common, e.g., in neuroscience, and edge bundling is one way to increase its readability or reveal hidden structures. This article presents a 3D extension to kernel density estimation-based edge bundling that is meant to be used in an interactive immersive analysis setting. This extension adds awareness of the edges’ direction when using kernel smoothing and thus implicitly supports both directed and undirected graphs. The method generates explicit bundles of edges, which can be analyzed and visualized individually and as sufficient as possible for a given application context, while it scales linearly with the input size.
@article{ZIELASKO2019,
title = "Voxel-based edge bundling through direction-aware kernel smoothing",
journal = "Computers & Graphics",
volume = "83",
pages = "87 - 96",
year = "2019",
issn = "0097-8493",
doi = "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cag.2019.06.008",
url = "http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0097849319301025",
author = "Daniel Zielasko and Xiaoqing Zhao and Ali Can Demiralp and Torsten W. Kuhlen and Benjamin Weyers"}
Interactive Level-of-Detail Visualization of 3D-Polarized Light Imaging Data Using Spherical Harmonics
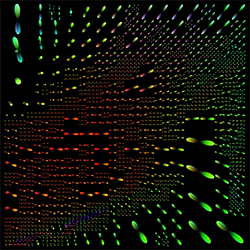
3D-Polarized Light Imaging (3D-PLI) provides data that enables an exploration of brain fibers at very high resolution. However, the visualization poses several challenges. Beside the huge data set sizes, users have to visually perceive the pure amount of information which might be, among other aspects, inhibited for inner structures because of occlusion by outer layers of the brain. We propose a clustering of fiber directions by means of spherical harmonics using a level-of-detail structure by which the user can interactively choose a clustering degree according to the zoom level or details required. Furthermore, the clustering method can be used for the automatic grouping of similar spherical harmonics automatically into one representative. An optional overlay with a direct vector visualization of the 3D-PLI data provides a better anatomical context.
Honorable Mention for Best Short Paper!
@inproceedings {Haenel2017Interactive,
booktitle = {EuroVis 2017 - Short Papers},
editor = {Barbora Kozlikova and Tobias Schreck and Thomas Wischgoll},
title = {{Interactive Level-of-Detail Visualization of 3D-Polarized Light Imaging Data Using Spherical Harmonics}},
author = {H\”anel, Claudia and Demiralp, Ali C. and Axer, Markus and Gr\”assel, David and Hentschel, Bernd and Kuhlen, Torsten W.},
year = {2017},
publisher = {The Eurographics Association},
ISBN = {978-3-03868-043-7},
DOI = {10.2312/eurovisshort.20171145}
}

